Hydroconstruct Inflatable Rubber Dams for Water Projects


Hydroconstruct designs, manufactures and installs inflatable rubber dams for hydropower, irrigation and flood protection applications.
Rubber dams or gates are flexible weir structures made of inflatable bladders. We offer both water and air-filled rubber dams. The design height of Hydroconstruct rubber dams ranges from 30cm to 4.5m, in both straight and curved axis designs.
Inflatable rubber dams systems for water projects
In principle, the pressure of water or air used to inflate the rubber bladder defines its height. The bladder is formed by a rubber membrane, which is directly clamped to the weir sill. Low maintenance costs are achieved through the lack of moving metal parts. Our membrane is vulcanised in one piece in a continuous process.
Rubber dams can consist of multiple segments that can form independent weir systems or link together to act as one system.
Our rubber material and the flexibility of the dam provide robust resistance against, and easy passage of, floating objects. Ice loading and freezing head ponds can be handled in a safe and controlled manner.
Water filled rubber dams
Water filled rubber dams are well-suited for headwater level regulation purposes and can be used, for instance, for hydropower applications. The maintenance of a constant headwater level is of interest for energy production at a hydropower site.
The feature of a strictly horizontal weir crest in all states allows a controlled lowering and rising of the rubber dam. Therefore, overflow at the dam can be accurately adjusted from none to the maximum flow, which is achieved if the rubber dam is fully deflated.
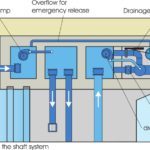
Important components of a Hydroconstruct water-filled rubber dam system are the control shaft and rubber membrane, both of which are connected by concrete embedded pipework. As integrated vessels, the pressure of the rubber bladder is visible in the control shaft system.
The system consists of a pump, filling, regulation and drainage shaft. If there is more the one independent weir system, there is a filling and a regulation shaft for each system. The pump and drainage shaft can be shared between these independent systems.
Rubber water dams filling and operations
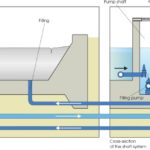
Rubber dams are filled by transferring water from the pump shaft into the filling shaft, where it will flow into the bladder. The dam is lowered by pumping water from the regulation shaft into the drainage shaft. This causes a gradient so water flows from the bladder into the regulation shaft.
For operation in winter with temperatures below freezing point water pumping patterns ensures safe operation.
The rubber dam is operated by a programmable logic controller (PLC). This can either be an autonomous system or integrated into power plant control. Many systems have an independent control setup and take defined parameters and triggers from the overhead control. Important parameters are the headwater level and the levels in the filling and regulation shaft.
The position of the weir crest is also measured. For information purposes, the flow over the rubber dam is calculated and displayed on the touch panel, which is the human-machine interface (HMI). It can also be sent along with other rubber dam parameters to overhead control.
Air filled rubber dams systems for hydropower operations
Rubber dams can also be filled using pressurised air, which are inflated using blowers.
Besides small differences in rubber dam design, the main variance is caused by different properties of air and water. Due to the lower density of air compared to water, the weir crest will form a V-notch if the pressure falls below a certain value. Therefore, air-filled rubber dams are better suited for operations in a fully inflated state, with occasional full deflation for continuous headwater level regulation.
Hydroconstruct rubber dams are versatile structures. If you have any further questions or wish to request a quotation, please send an enquiry though this page.